扩展教程#
JupyterLab 扩展为用户体验增添了功能。本页描述了如何创建一种类型的扩展,即一个 应用程序插件,它将:
在 命令面板 侧边栏添加一个“随机天文图片”命令
激活时获取图片和元数据
在选项卡面板中显示图片和元数据
通过本教程,您将学习到:
如何在 Linux 或 OSX 机器上从头开始设置扩展开发环境。(如果您使用 Windows,您需要稍微修改命令。)
如何从 jupyterlab/extension-template 开始一个扩展项目
如何在 JupyterLab 中迭代地编码、构建和加载您的扩展
如何使用 git 进行版本控制
如何发布您的扩展供他人使用
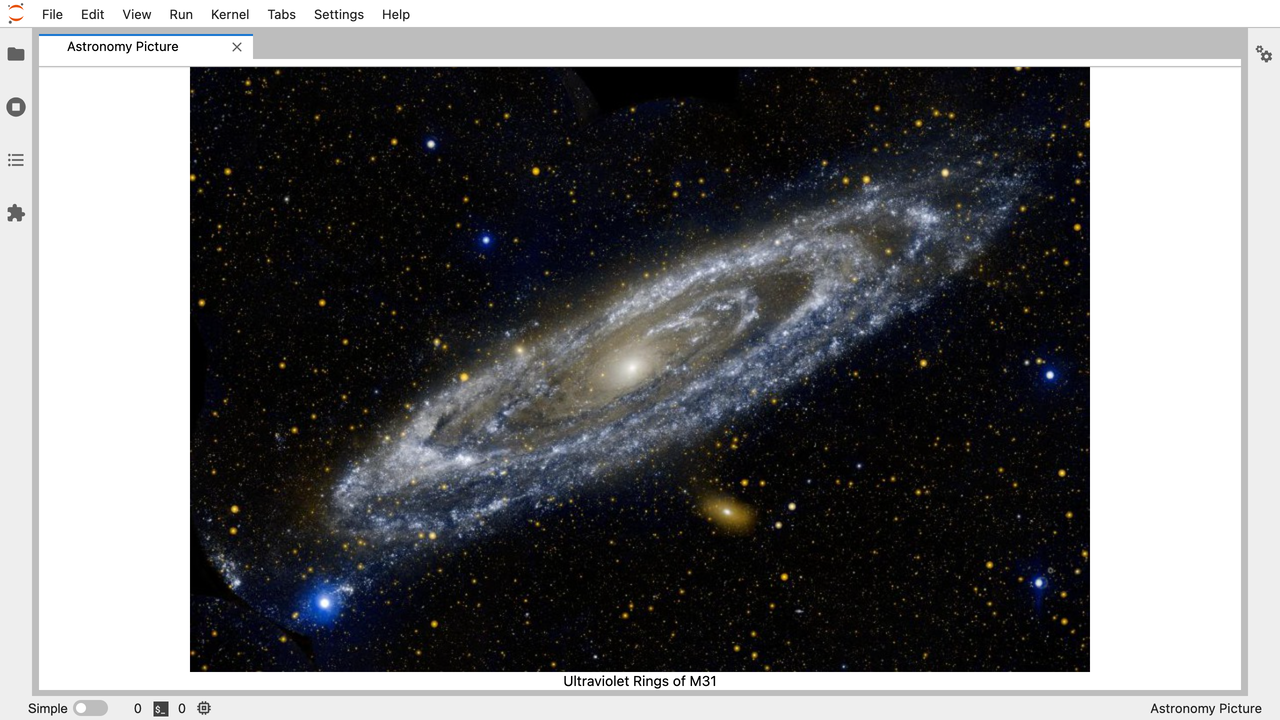
完成的扩展,显示2015年7月24日的天文每日图片。#
听起来很有趣?太棒了。我们开始吧!
设置开发环境#
使用 miniconda 安装 conda#
首先,按照Conda 的安装文档安装 miniconda。
在 conda 环境中安装 NodeJS、JupyterLab 等#
接下来创建一个包含以下内容的 conda 环境:
最新版本的 JupyterLab
copier 和一些依赖项,您将使用它来引导您的扩展项目结构(这是一个 Python 工具,我们将在下面使用 conda 安装)。
NodeJS,您将用来编译扩展的 Web 资源(例如 TypeScript、CSS)的 JavaScript 运行时
git,一个版本控制系统,您将在本教程中用来记录您的工作快照
最佳实践是保留根 conda 环境(即 miniconda 安装程序创建的环境)不变,并在命名为 conda 环境中安装您项目特定的依赖项。运行此命令以创建一个名为 jupyterlab-ext 的新环境。
conda create -n jupyterlab-ext --override-channels --strict-channel-priority -c conda-forge -c nodefaults jupyterlab=4 nodejs=20 git copier=9 jinja2-time --yes
现在激活新环境,以便您运行的所有后续命令都在该环境中执行。
conda activate jupyterlab-ext
注意:您需要在每个新打开的终端中运行上述命令,然后才能使用您在 jupyterlab-ext 环境中安装的工具。
创建一个仓库#
为您的扩展创建一个新仓库(例如,参见 GitHub 说明)。这是可选步骤,但如果您想分享您的扩展,强烈建议这样做。
创建扩展项目#
从模板初始化项目#
接下来使用 copier 为您的扩展创建一个新项目。这将在您当前目录中为您的扩展创建一个新文件夹。
mkdir my_first_extension
cd my_first_extension
copier copy --trust https://github.com/jupyterlab/extension-template .
在提示时,为所有模板提示输入如下值(apod 代表 Astronomy Picture of the Day,我们用于获取图片的 NASA 服务)。
What is your extension kind?
(Use arrow keys)
frontend
Extension author name
Your Name
Extension author email
your@name.org
JavaScript package name
jupyterlab_apod
Python package name
jupyterlab_apod
Extension short description
Show a random NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day in a JupyterLab panel
Does the extension have user settings?
N
Do you want to set up Binder example?
Y
Do you want to set up test for the extension?
Y
Git remote repository URL
https://github.com/github_username/jupyterlab_apod
注意
如果您不使用仓库,请将仓库字段留空。您可以稍后回到
package.json文件中编辑仓库字段。如果您使用的是最新版本的模板,您会注意到模板中包含了测试。如果您不想包含它们,只需对测试提示回答
n。
列出文件。
ls -a
您应该看到如下列表。
.copier-answers.yml .github .gitignore .prettierignore .yarnrc.yml
babel.config.js jest.config.js pyproject.toml src ui-tests
binder jupyterlab_apod README.md style yarn.lock
CHANGELOG.md LICENSE RELEASE.md tsconfig.json
install.json package.json setup.py tsconfig.test.json
将您拥有的提交到 git#
在您的 jupyterlab_apod 文件夹中运行以下命令,将其初始化为 git 仓库并提交当前代码。
git init
git add .
git commit -m 'Seed apod project from extension template'
注意
此步骤在技术上不是必需的,但将更改记录在版本控制系统中是一个好习惯,以防您需要回滚到早期版本或想与他人协作。您可以将本教程中的工作与 GitHub 上 jupyterlab/jupyterlab_apod 中 jupyterlab_apod 参考版本中的提交进行比较。
构建并安装用于开发的扩展#
您的新扩展项目中有足够的代码,可以在 JupyterLab 中看到它的工作。运行以下命令以安装初始项目依赖项并将扩展安装到 JupyterLab 环境中。
pip install -ve .
上述命令将扩展的前端部分复制到 JupyterLab 中。每次我们进行更改时,我们都可以再次运行此 pip install 命令,将更改复制到 JupyterLab 中。更好的是,我们可以使用 develop 命令创建从 JupyterLab 到我们源目录的符号链接。这意味着我们的更改会自动在 JupyterLab 中可用。
jupyter labextension develop --overwrite .
Windows 用户注意事项#
重要
在 Windows 上,对于 Python 3.8 或更高版本,符号链接需要在 Windows 10 或更高版本上通过激活“开发人员模式”才能激活。这可能不被您的管理员允许。请参阅 在 Windows 上激活开发人员模式 以获取说明。
查看初始扩展的实际效果#
安装完成后,打开第二个终端。运行以下命令以激活 jupyterlab-ext 环境并在您的默认 Web 浏览器中启动 JupyterLab。
conda activate jupyterlab-ext
jupyter lab
在该浏览器窗口中,按照您的浏览器说明打开 JavaScript 控制台
在控制台打开的情况下重新加载页面后,您应该会看到一条消息,显示 JupyterLab extension jupyterlab_apod is activated!。如果看到了,恭喜您,您可以开始修改扩展了!如果没有,请回去确保您没有遗漏任何步骤,如果遇到困难,请寻求帮助。
注意
保持运行 jupyter lab 命令的终端和运行 JupyterLab 的状态,以便查看下面更改的效果。
添加一个每日天文图片小部件#
显示一个空面板#
命令面板 是 JupyterLab 中所有可用命令的主要视图。您的第一次添加,您将在面板中添加一个 随机天文图片 命令,并让它在调用时显示一个 天文图片 选项卡面板。
启动您最喜欢的文本编辑器并打开您的扩展项目中的 src/index.ts 文件。更改文件顶部的导入以获取命令面板接口和 JupyterFrontEnd 实例的引用。
import {
JupyterFrontEnd,
JupyterFrontEndPlugin
} from '@jupyterlab/application';
import { ICommandPalette } from '@jupyterlab/apputils';
找到类型为 JupyterFrontEndPlugin 的 plugin 对象。更改定义,使其如下所示:
/**
* Initialization data for the jupyterlab_apod extension.
*/
const plugin: JupyterFrontEndPlugin<void> = {
id: 'jupyterlab-apod',
description: 'Show a random NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day in a JupyterLab panel.',
autoStart: true,
requires: [ICommandPalette],
activate: (app: JupyterFrontEnd, palette: ICommandPalette) => {
console.log('JupyterLab extension jupyterlab_apod is activated!');
console.log('ICommandPalette:', palette);
}
};
requires 属性表示您的插件在启动时需要一个实现 ICommandPalette 接口的对象。JupyterLab 会将 ICommandPalette 的实例作为 activate 的第二个参数传递,以满足此要求。palette: ICommandPalette 的定义使此实例在该函数中可供您的代码使用。第二个 console.log 行的存在只是为了让您可以立即检查您的更改是否有效。
现在您需要安装这些依赖项。在仓库根文件夹中运行以下命令以安装依赖项并将其保存到您的 package.json 中。
jlpm add @jupyterlab/apputils @jupyterlab/application
最后,运行以下命令来重新构建您的扩展。
jlpm run build
注意
本教程使用 jlpm 安装 Javascript 包并运行构建命令,这是 JupyterLab 捆绑的 yarn 版本。如果您愿意,可以使用其他 Javascript 包管理器,如 npm 或 yarn 本身。
扩展构建完成后,返回您启动 JupyterLab 时打开的浏览器选项卡。刷新它并在控制台中查看。您应该会看到与之前相同的激活消息,以及您刚刚添加的关于 ICommandPalette 实例的新消息。如果没有,请检查构建命令的输出中是否有错误并更正您的代码。
JupyterLab extension jupyterlab_apod is activated!
ICommandPalette: Palette {_palette: CommandPalette}
请注意,我们必须运行 jlpm run build 才能更新捆绑包。此命令执行两件事:将 src/` 中的 TypeScript 文件编译为 lib/ 中的 JavaScript 文件 (jlpm run build),然后将 lib/ 中的 JavaScript 文件捆绑为 jupyterlab_apod/static 中的 JupyterLab 扩展 (jlpm run build:extension)。如果您希望避免在每次更改后运行 jlpm run build,您可以打开第三个终端,激活 jupyterlab-ext 环境,并从您的扩展目录运行 jlpm run watch 命令,它将自动编译已更改和保存的 TypeScript 文件。
现在回到你的编辑器。修改文件顶部的导入,再添加一些导入
import { ICommandPalette, MainAreaWidget } from '@jupyterlab/apputils';
import { Widget } from '@lumino/widgets';
也安装这个新依赖项
jlpm add @lumino/widgets
然后再次修改插件对象内部的 activate 函数,使其具有以下代码 (高亮显示的行显示了 activate 函数,您只修改该函数的内容,因此请确保您的花括号匹配,并保持下方 export default plugin 部分不变)
const plugin: JupyterFrontEndPlugin<void> = {
id: 'jupyterlab-apod',
description: 'Show a random NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day in a JupyterLab panel.',
autoStart: true,
requires: [ICommandPalette],
activate: (app: JupyterFrontEnd, palette: ICommandPalette) => {
console.log('JupyterLab extension jupyterlab_apod is activated!');
// Define a widget creator function,
// then call it to make a new widget
const newWidget = () => {
// Create a blank content widget inside of a MainAreaWidget
const content = new Widget();
const widget = new MainAreaWidget({ content });
widget.id = 'apod-jupyterlab';
widget.title.label = 'Astronomy Picture';
widget.title.closable = true;
return widget;
}
let widget = newWidget();
// Add an application command
const command: string = 'apod:open';
app.commands.addCommand(command, {
label: 'Random Astronomy Picture',
execute: () => {
// Regenerate the widget if disposed
if (widget.isDisposed) {
widget = newWidget();
}
if (!widget.isAttached) {
// Attach the widget to the main work area if it's not there
app.shell.add(widget, 'main');
}
// Activate the widget
app.shell.activateById(widget.id);
}
});
// Add the command to the palette.
palette.addItem({ command, category: 'Tutorial' });
}
};
export default plugin;
第一个新代码块定义(并调用)一个可重用的 widget 创建函数。该函数返回一个 MainAreaWidget 实例,该实例将其子级作为空的 content Widget。它还为主要区域 widget 分配一个唯一的 ID,为其提供一个将显示为选项卡标题的标签,并使该选项卡可以由用户关闭。第二个代码块添加了一个新命令,其 ID 为 apod:open,标签为 Random Astronomy Picture 到 JupyterLab。当命令执行时,它会检查 widget 是否未被处置,如果 widget 不存在,则将其附加到主显示区域,然后使其成为活动选项卡。最后一行新代码使用命令 ID 将命令添加到命令面板中,位于名为 Tutorial 的部分。
再次使用 jlpm run build 构建您的扩展(除非您已经在使用 jlpm run watch),然后刷新浏览器选项卡。通过单击“视图”菜单中的“命令”或使用键盘快捷键 Command/Ctrl Shift C 打开命令面板,并在搜索框中键入 Astronomy。您的 Random Astronomy Picture 命令应该会出现。单击它或使用键盘选择它并按 Enter。您应该会看到一个带有选项卡标题 Astronomy Picture 的新的空白面板。单击选项卡上的 x 关闭它并再次激活命令。选项卡应该会重新出现。最后,单击启动器选项卡之一,以便 Astronomy Picture 面板仍然打开但不再活动。现在再次运行 Random Astronomy Picture 命令。单个 Astronomy Picture 选项卡应该会移到前景。
正在进行中的扩展,显示一个空白面板。#
如果您的 widget 行为不正常,请将您的代码与 01-show-a-panel 标签处的参考项目状态进行比较。一旦您将所有内容都正常工作,就 git 提交您的更改并继续。
git add package.json src/index.ts
git commit -m 'Show Astronomy Picture command in palette'
在面板中显示图片#
您现在有一个空面板。是时候向其中添加图片了。返回您的代码编辑器。在创建 MainAreaWidget 实例的行下方和返回新 widget 的行上方,在 widget 创建器函数中添加以下代码。
// Add an image element to the content
let img = document.createElement('img');
content.node.appendChild(img);
// Get a random date string in YYYY-MM-DD format
function randomDate() {
const start = new Date(2010, 1, 1);
const end = new Date();
const randomDate = new Date(start.getTime() + Math.random()*(end.getTime() - start.getTime()));
return randomDate.toISOString().slice(0, 10);
}
// Fetch info about a random picture
const response = await fetch(`https://api.nasa.gov/planetary/apod?api_key=DEMO_KEY&date=${randomDate()}`);
const data = await response.json() as APODResponse;
if (data.media_type === 'image') {
// Populate the image
img.src = data.url;
img.title = data.title;
} else {
console.log('Random APOD was not a picture.');
}
前两行创建一个新的 HTML <img> 元素并将其添加到 widget DOM 节点。接下来的行定义一个函数,以 YYYY-MM-DD 格式获取一个随机日期,然后该函数用于使用 HTML fetch API 发出请求,该请求返回有关该日期每日天文图片的信息。最后,我们根据响应设置图像源和标题属性。
现在定义上面代码中引入的 APODResponse 类型。将此定义放在文件顶部导入的下方。
interface APODResponse {
copyright: string;
date: string;
explanation: string;
media_type: 'video' | 'image';
title: string;
url: string;
};
然后我们需要在代码的几个地方添加 async 和 await,因为我们在 widget 创建器函数中使用了 await。
首先,将 activate 方法更新为 async。
activate: async (app: JupyterFrontEnd, palette: ICommandPalette) => {
接下来,将 newWidget 函数更新为 async。
const newWidget = async () => {
最后,在两个 newWidget 函数调用中都添加 await,并在 execute 函数中添加 async。
let widget = await newWidget();
// Add an application command
const command: string = 'apod:open';
app.commands.addCommand(command, {
label: 'Random Astronomy Picture',
execute: async () => {
// Regenerate the widget if disposed
if (widget.isDisposed) {
widget = await newWidget();
}
if (!widget.isAttached) {
// Attach the widget to the main work area if it's not there
app.shell.add(widget, 'main');
}
// Activate the widget
app.shell.activateById(widget.id);
}
});
注意
如果您是 JavaScript / TypeScript 新手,并且想了解更多关于 async、await 和 Promises 的信息,您可以查看 MDN 上的此教程。
请务必也参考 另请参阅 部分中的其他资源,以获取更多材料。
如有必要,重新构建您的扩展 (jlpm run build),刷新您的浏览器选项卡,然后再次运行 随机天文图片 命令。现在,当面板打开时,您应该会看到一张图片(如果该随机日期有图片而不是视频)。
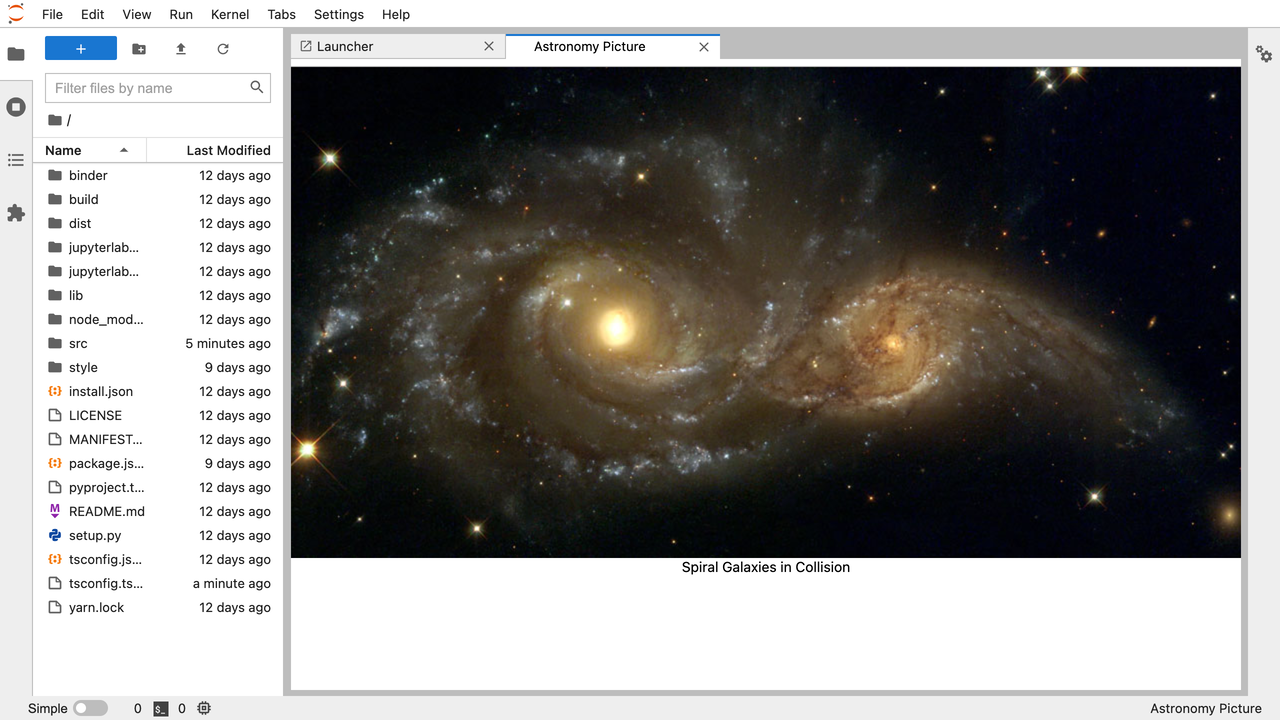
正在进行中的扩展,显示2014年1月19日的天文每日图片。#
请注意,图像未在面板中居中,如果图像大于面板区域,面板也不会滚动。您将在接下来的部分中解决这两个问题。
如果您根本没有看到图像,请将您的代码与参考项目中的 02-show-an-image 标签进行比较。当它工作时,再次进行 git 提交。
git add src/index.ts
git commit -m 'Show a picture in the panel'
改善小部件行为#
居中图像,添加归属和错误消息#
打开扩展项目目录中的 style/base.css 进行编辑。向其中添加以下行。
.my-apodWidget {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
overflow: auto;
}
此 CSS 将内容在 widget 面板内垂直堆叠,并在内容溢出时允许面板滚动。由于 package.json 文件中有一个指向它的 style 字段,因此 JupyterLab 会自动将此 CSS 文件包含在页面中。通常,您应该将所有样式导入到单个 CSS 文件中,例如此 index.css 文件,并将该 CSS 文件的路径放在 package.json 文件的 style 字段中。
返回 index.ts 文件。修改 activate 函数以应用 CSS 类、版权信息和 API 响应的错误处理。您将更新和替换/删除一些行,因此函数的开头应该如下所示:
activate: async (app: JupyterFrontEnd, palette: ICommandPalette) => {
console.log('JupyterLab extension jupyterlab_apod is activated!');
// Define a widget creator function,
// then call it to make a new widget
const newWidget = async () => {
// Create a blank content widget inside of a MainAreaWidget
const content = new Widget();
content.addClass('my-apodWidget');
const widget = new MainAreaWidget({ content });
widget.id = 'apod-jupyterlab';
widget.title.label = 'Astronomy Picture';
widget.title.closable = true;
// Add an image element to the content
let img = document.createElement('img');
content.node.appendChild(img);
let summary = document.createElement('p');
content.node.appendChild(summary);
// Get a random date string in YYYY-MM-DD format
function randomDate() {
const start = new Date(2010, 1, 1);
const end = new Date();
const randomDate = new Date(start.getTime() + Math.random()*(end.getTime() - start.getTime()));
return randomDate.toISOString().slice(0, 10);
}
// Fetch info about a random picture
const response = await fetch(`https://api.nasa.gov/planetary/apod?api_key=DEMO_KEY&date=${randomDate()}`);
if (!response.ok) {
const data = await response.json();
if (data.error) {
summary.innerText = data.error.message;
} else {
summary.innerText = response.statusText;
}
} else {
const data = await response.json() as APODResponse;
if (data.media_type === 'image') {
// Populate the image
img.src = data.url;
img.title = data.title;
summary.innerText = data.title;
if (data.copyright) {
summary.innerText += ` (Copyright ${data.copyright})`;
}
} else {
summary.innerText = 'Random APOD fetched was not an image.';
}
}
return widget;
}
// Keep all the remaining lines below the newWidget function
// definition the same as before from here down ...
注意
如果您的图像面板一直显示错误消息,您可能需要更新您的 NASA API 密钥(过多的图像请求可能会超出您的限制)。
如有必要,构建您的扩展程序 (jlpm run build) 并刷新您的 JupyterLab 浏览器选项卡。调用 随机天文图片 命令并确认图片居中,下方有版权信息。调整浏览器窗口或面板大小,使图片大于可用区域。确保您可以滚动面板以查看图片的整个区域。
如果任何功能不正常,请将您的代码与参考项目 03-style-and-attribute 标签进行比较。当一切正常时,再次提交。
git add style/base.css src/index.ts
git commit -m 'Add styling, attribution, error handling'
按需显示新图像#
activate 函数已经变得相当长了,还有更多的功能需要添加。让我们将代码重构为两个独立的部分:
一个
APODWidget,它封装了天文图片面板元素、配置以及即将添加的更新行为。一个
activate函数,它将 widget 实例添加到 UI 并决定何时刷新图片。
首先,将 widget 代码重构为新的 APODWidget 类。
将该类添加到 index.ts 文件中 APODResponse 定义的正下方。
class APODWidget extends Widget {
/**
* Construct a new APOD widget.
*/
constructor() {
super();
this.addClass('my-apodWidget');
// Add an image element to the panel
this.img = document.createElement('img');
this.node.appendChild(this.img);
// Add a summary element to the panel
this.summary = document.createElement('p');
this.node.appendChild(this.summary);
}
/**
* The image element associated with the widget.
*/
readonly img: HTMLImageElement;
/**
* The summary text element associated with the widget.
*/
readonly summary: HTMLParagraphElement;
/**
* Handle update requests for the widget.
*/
async updateAPODImage(): Promise<void> {
const response = await fetch(`https://api.nasa.gov/planetary/apod?api_key=DEMO_KEY&date=${this.randomDate()}`);
if (!response.ok) {
const data = await response.json();
if (data.error) {
this.summary.innerText = data.error.message;
} else {
this.summary.innerText = response.statusText;
}
return;
}
const data = await response.json() as APODResponse;
if (data.media_type === 'image') {
// Populate the image
this.img.src = data.url;
this.img.title = data.title;
this.summary.innerText = data.title;
if (data.copyright) {
this.summary.innerText += ` (Copyright ${data.copyright})`;
}
} else {
this.summary.innerText = 'Random APOD fetched was not an image.';
}
}
/**
* Get a random date string in YYYY-MM-DD format.
*/
randomDate(): string {
const start = new Date(2010, 1, 1);
const end = new Date();
const randomDate = new Date(start.getTime() + Math.random()*(end.getTime() - start.getTime()));
return randomDate.toISOString().slice(0, 10);
}
}
您以前写过所有代码。您所做的只是重组它以使用实例变量并将图像请求移动到其自己的函数中。
接下来,将 activate 中剩余的逻辑移到一个新的顶级函数中,该函数位于 APODWidget 类定义的正下方。修改代码,以便当主 JupyterLab 区域中不存在 widget 时创建 widget,或者当命令再次运行时刷新现有 widget 中的图像。这些更改后,activate 函数的代码应如下所示:
/**
* Activate the APOD widget extension.
*/
function activate(app: JupyterFrontEnd, palette: ICommandPalette) {
console.log('JupyterLab extension jupyterlab_apod is activated!');
// Define a widget creator function
const newWidget = () => {
const content = new APODWidget();
const widget = new MainAreaWidget({content});
widget.id = 'apod-jupyterlab';
widget.title.label = 'Astronomy Picture';
widget.title.closable = true;
return widget;
}
// Create a single widget
let widget = newWidget();
// Add an application command
const command: string = 'apod:open';
app.commands.addCommand(command, {
label: 'Random Astronomy Picture',
execute: () => {
// Regenerate the widget if disposed
if (widget.isDisposed) {
widget = newWidget();
}
if (!widget.isAttached) {
// Attach the widget to the main work area if it's not there
app.shell.add(widget, 'main');
}
// Refresh the picture in the widget
widget.content.updateAPODImage();
// Activate the widget
app.shell.activateById(widget.id);
}
});
// Add the command to the palette.
palette.addItem({ command, category: 'Tutorial' });
}
从 JupyterFrontEndPlugin 对象中删除 activate 函数定义,并改为引用顶级函数,如下所示:
const plugin: JupyterFrontEndPlugin<void> = {
id: 'jupyterlab_apod',
autoStart: true,
requires: [ICommandPalette],
activate: activate
};
请确保文件中保留 export default plugin; 行。现在再次构建扩展并刷新 JupyterLab 浏览器选项卡。在不关闭面板的情况下多次运行 随机天文图片 命令。每次执行命令时,图片都应该更新。关闭面板,运行命令,它应该重新出现并显示一张新图片。
如果任何功能不正常,请将您的代码与 04-refactor-and-refresh 标签进行比较以进行调试。一旦它正常工作,就提交它。
git add src/index.ts
git commit -m 'Refactor, refresh image'
当浏览器刷新时恢复面板状态#
您可能会注意到,每次刷新浏览器选项卡时,天文图片面板都会消失,即使在刷新之前它是打开的。其他打开的面板,如笔记本、终端和文本编辑器,都会重新出现并返回到您在面板布局中离开它们的位置。您也可以让您的扩展以这种方式运行。
更新 index.ts 文件顶部的导入,使整个导入语句列表如下所示(添加 ILayoutRestorer 和 WidgetTracker)
import {
ILayoutRestorer,
JupyterFrontEnd,
JupyterFrontEndPlugin
} from '@jupyterlab/application';
import {
ICommandPalette,
MainAreaWidget,
WidgetTracker
} from '@jupyterlab/apputils';
import { Widget } from '@lumino/widgets';
然后将 ILayoutRestorer 接口作为 optional 添加到 JupyterFrontEndPlugin 定义中。此添加将全局 LayoutRestorer 作为 activate 函数的第三个参数传递。
const plugin: JupyterFrontEndPlugin<void> = {
id: 'jupyterlab-apod',
description: 'Show a random NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day in a JupyterLab panel.',
autoStart: true,
requires: [ICommandPalette],
optional: [ILayoutRestorer],
activate: activate
};
这里 ILayoutRestorer 被指定为一个 optional 令牌,因为相应的服务可能在不提供布局恢复功能的定制 JupyterLab 分发中不可用。将其设置为 optional 使其成为一个有益的功能,并使您的扩展能够在更多基于 JupyterLab 的应用程序中加载。
注意
您可以在扩展开发者指南的令牌部分了解更多关于 requires 和 optional 的信息。
最后,重写 activate 函数,使其:
声明一个 widget 变量,但不立即创建实例。
将全局
LayoutRestorer作为activate函数的第三个参数。此参数声明为ILayoutRestorer | null,因为令牌被指定为optional。构建一个
WidgetTracker并告知ILayoutRestorer使用它来保存/恢复面板状态。适当地创建、跟踪、显示和刷新 widget 面板。
function activate(app: JupyterFrontEnd, palette: ICommandPalette, restorer: ILayoutRestorer | null) {
console.log('JupyterLab extension jupyterlab_apod is activated!');
// Declare a widget variable
let widget: MainAreaWidget<APODWidget>;
// Add an application command
const command: string = 'apod:open';
app.commands.addCommand(command, {
label: 'Random Astronomy Picture',
execute: () => {
if (!widget || widget.isDisposed) {
const content = new APODWidget();
widget = new MainAreaWidget({content});
widget.id = 'apod-jupyterlab';
widget.title.label = 'Astronomy Picture';
widget.title.closable = true;
}
if (!tracker.has(widget)) {
// Track the state of the widget for later restoration
tracker.add(widget);
}
if (!widget.isAttached) {
// Attach the widget to the main work area if it's not there
app.shell.add(widget, 'main');
}
widget.content.updateAPODImage();
// Activate the widget
app.shell.activateById(widget.id);
}
});
// Add the command to the palette.
palette.addItem({ command, category: 'Tutorial' });
// Track and restore the widget state
let tracker = new WidgetTracker<MainAreaWidget<APODWidget>>({
namespace: 'apod'
});
if (restorer) {
restorer.restore(tracker, {
command,
name: () => 'apod'
});
}
}
最后一次重建您的扩展并刷新浏览器选项卡。执行 随机天文图片 命令并验证面板是否带有一张图片出现。再次刷新浏览器选项卡。您应该会立即看到一个天文图片面板重新出现,而无需运行该命令。关闭面板并刷新浏览器选项卡。然后,刷新后您应该看不到天文图片选项卡。

完成的扩展,显示2015年7月24日的天文每日图片。#
如果您的扩展程序无法正常工作,请参阅 05-restore-panel-state 标签进行调试。当您的扩展程序状态正常持久化时,进行一次提交。
git add src/index.ts
git commit -m 'Restore panel state'
恭喜!您已经实现了本教程开头列出的所有行为。
打包您的扩展#
JupyterLab 3.0 及以上版本的 JupyterLab 扩展可以作为 Python 包分发。我们使用的扩展模板在 pyproject.toml 文件中包含了所有 Python 打包说明,以便将您的扩展封装在一个 Python 包中。在生成包之前,我们首先需要安装 build。
pip install build
要在 dist/ 目录中创建 Python 源包 (.tar.gz),请执行:
python -m build -s
要在 dist/ 目录中创建 Python wheel 包 (.whl),请执行:
python -m build
这两个命令都将 JavaScript 构建到 jupyterlab_apod/labextension/static 目录中的捆绑包中,然后与 Python 包一起分发。此捆绑包也将包含任何必要的 JavaScript 依赖项。您可能希望在 jupyterlab_apod/labextension/static 目录中查看,以保留您的包中分发的 JavaScript 记录,或者您可能希望将此“构建产物”从您的源代码仓库历史中排除。
您现在可以尝试像用户一样安装您的扩展。打开一个新终端并运行以下命令来创建一个新环境并安装您的扩展。
conda create -n jupyterlab-apod jupyterlab
conda activate jupyterlab-apod
pip install jupyterlab_apod/dist/jupyterlab_apod-0.1.0-py3-none-any.whl
jupyter lab
您应该会看到一个新的 JupyterLab 浏览器选项卡出现。出现后,执行 随机天文图片 命令以检查您的扩展是否正常工作。
发布您的扩展#
您可以将您的 Python 包发布到 PyPI 或 conda-forge 仓库,以便用户可以使用 pip 或 conda 轻松安装扩展。
您可能还会出于以下几个原因将您的扩展作为 JavaScript 包发布到 npm 包仓库:
将扩展作为 npm 包分发允许用户明确地将扩展编译到 JupyterLab 中(类似于 JupyterLab 1 和 2 版本中的做法),这可以产生更优化的 JupyterLab 包。
正如我们上面看到的,JupyterLab 使扩展能够使用其他扩展提供的服务。例如,我们上面的扩展使用了 JupyterLab 核心扩展提供的
ICommandPalette和ILayoutRestorer服务。我们通过从@jupyterlab/apputils和@jupyterlab/applicationnpm 包中导入它们的令牌,并在插件定义中列出它们,从而告诉 JupyterLab 我们需要这些服务。如果您想为 JupyterLab 系统提供服务供其他扩展使用,您需要将您的 JavaScript 包发布到 npm,以便其他扩展可以依赖它并导入和要求您的令牌。
自动化发布#
如果您使用模板引导您的扩展,则仓库应该已经与 Jupyter Releaser 兼容。
Jupyter Releaser 提供了一组 GitHub Actions 工作流来:
在更新日志中生成一个新条目
草拟一个新版本
将版本发布到
PyPI和npm
有关如何运行发布工作流的更多信息,请查看文档:jupyter-server/jupyter_releaser
了解更多#
您已完成本教程。干得好!如果您想继续学习,这里有一些建议可以尝试: